Clear structure is important to improve document accessibility
These guidelines and screenshots apply specifically to Microsoft Word 2013 on Windows. There may be differences when applying the techniques in other versions of Microsoft Word.
Provide appropriate heading structure for a document
Heading structures with a distinct, visual style help individuals with visual impairments understand how a document is organized. Appropriate headings also act as secondary navigation tools that help readers skim and scan the document.
Headings should fit an outline. Making text larger or bolder does not make it a heading in Word.
Add headings to a document
Use the built-in heading styles to apply uniform heading structure to Word documents.
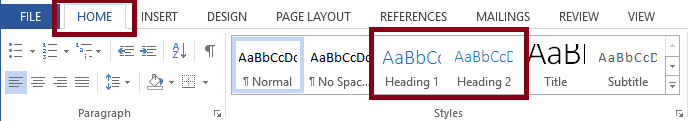
Word Styles contain preconfigured headings understood by assistive technology (e.g., Heading 1- Heading 6). These headings are available under the Styles section in the Home tab of the Ribbon.
Apply the “Heading 1” style for the main heading and “Heading 2” for sub-headings. Additional organization and division of topics should use the appropriate head style: “Heading 3,” “Heading 4,” etc. without going past "Heading 6."